How Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) is Transforming the Fintech Market
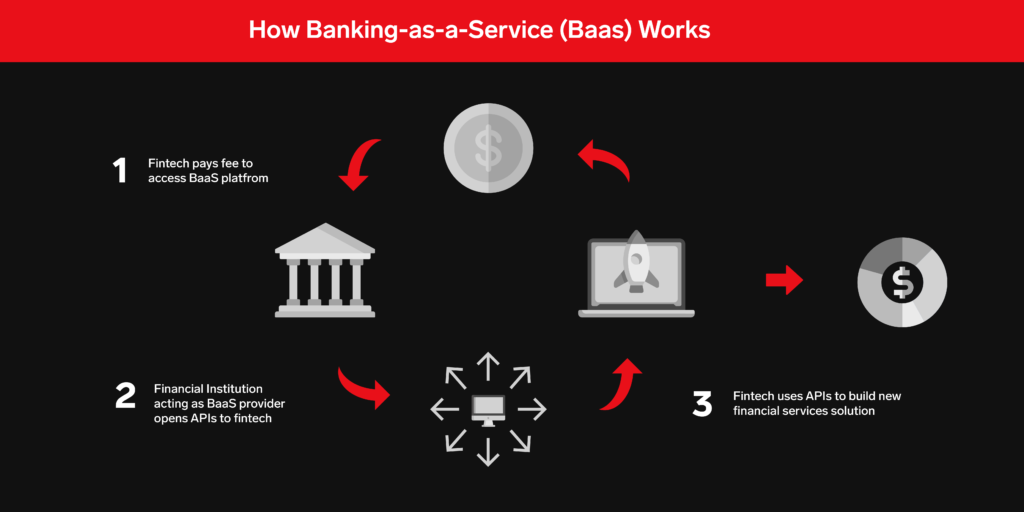
Why Is BaaS Important?
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) is a game-changer for the financial industry, particularly for fintech companies looking to disrupt traditional banking models. Here’s why BaaS holds such significance in today’s market:
- Lower Barriers to Entry
Historically, launching banking services required companies to invest in the expensive and lengthy process of becoming a licensed bank. With BaaS, even non-financial companies can offer financial services without having to navigate the complexities of banking regulations. This dramatically lowers the barrier to entry, enabling more businesses to participate in the financial services market.
- Accelerating Fintech Innovation
By leveraging BaaS platforms, fintechs can focus on creating innovative customer experiences rather than spending resources on infrastructure development. This opens the door to new product offerings like digital wallets, instant payments, and embedded financing solutions. BaaS has helped to supercharge fintech growth, leading to faster innovation cycles and the creation of more tailored services for consumers and businesses alike.
- Cost Efficiency
Building a traditional banking infrastructure from scratch is costly and time-consuming. BaaS offers a cost-effective alternative by providing ready-to-use banking infrastructure that companies can easily plug into. This enables companies to bring financial products to market faster and at a significantly lower cost.
- Enhanced Customer Experience
By integrating banking services into existing platforms, BaaS enables companies to offer seamless, embedded experiences for users. Whether it’s through a ride-hailing app, an e-commerce platform, or a financial services app, users can manage their finances without leaving the ecosystem they’re already familiar with, improving overall customer satisfaction and engagement.
- Financial Inclusion
BaaS plays a crucial role in increasing financial inclusion, especially in underbanked regions. Fintechs using BaaS can reach a wider audience by providing digital-first banking services that are more accessible to people who might not have traditional bank accounts.
Overall, BaaS is reshaping the future of banking, providing companies with the tools they need to innovate quickly while allowing traditional banks to tap into new revenue streams through partnerships with fintech firms.
The Role of APIs in BaaS
At the heart of the Banking-as-a-Service revolution lies the power of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
APIs are the building blocks that enable seamless communication between different software systems, allowing fintech companies to access and utilise the core infrastructure of licensed banks. Without APIs, the BaaS model wouldn’t be possible.
By leveraging APIs, BaaS enables FinTech’s and non-banking companies to offer a wide array of financial services with ease, speed, and cost-effectiveness. APIs have become the backbone of the fintech revolution, allowing businesses to innovate rapidly, while also providing customers with more choices and better services.
Real-World Use Cases of BaaS
The BaaS model has rapidly evolved from a niche concept to a driving force in fintech, with numerous companies leveraging BaaS to create innovative financial solutions. These use cases span across industries, from e-commerce and travel to financial management and digital wallets.
Below are some key real-world examples of how BaaS is transforming various sectors:
- Digital Wallets and Payments
Many fintech companies have utilised BaaS to offer customers digital wallets that combine traditional banking functions with modern convenience. Through their BaaS partnerships with banks, these companies can provide services like:
- Instant payments: Customers can send and receive money in real time.
- Multi-currency accounts: Users can hold, transfer, and convert funds in multiple currencies without needing multiple bank accounts.
- Fee-free transactions: By partnering with BaaS providers, companies can avoid hefty banking fees and pass these savings on to their customers.
- Embedded Finance in E-Commerce
E-commerce platforms are increasingly embedding financial services into their ecosystems through BaaS. This allows merchants to offer financing options, embedded payment solutions, and even loyalty programs without needing to partner with a bank directly. Examples include:
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL): Some use BaaS to offer instalment-based payment options directly through e-commerce checkout pages, providing seamless financing options for consumers.
- Instant Payouts: Platforms like AdhishwarPay can provide instant payouts to merchants, enabling faster access to funds after a sale, thanks to their integration with BaaS-powered solutions.
- Neobanks
Neobanks, or digital-only banks, are one of the most prominent examples of BaaS in action. Companies offer full banking services without being traditional banks themselves. By using BaaS platforms, these neobanks can provide:
- Bank accounts and cards: Users can open accounts, manage their finances, and receive debit cards, all through a fully digital experience.
- Loans and overdraft facilities: Neobanks leverage BaaS infrastructure to extend credit, offer loans, or provide overdraft protection without holding banking licenses themselves.
These neobanks use BaaS to provide a modern banking experience that prioritises speed, convenience, and transparency, attracting millions of users globally.
- Lending Platforms
BaaS has enabled the rapid growth of peer-to-peer lending platforms and alternative financing solutions. Companies utilise BaaS to offer loan origination, payments, and credit scoring services. BaaS allows these platforms to:
- Facilitate loans between borrowers and lenders without being the lender themselves.
- Automate credit assessments and loan disbursements through partnerships with traditional banks.
By tapping into BaaS, these platforms can focus on customer acquisition, risk management, and user experience while relying on the BaaS provider for banking operations.
- Financial Management Tools
Businesses offering financial management services can also benefit from BaaS by integrating banking functionalities directly into their platforms. For instance:
- Personal finance apps like BaaS to allow users to link bank accounts, track spending, and manage their budgets without leaving the app.
- Small business tools: Platforms integrate banking and payments into their accounting services, allowing businesses to manage invoices, receive payments, and handle payroll seamlessly.
BaaS provides these platforms with the banking infrastructure they need to offer comprehensive financial services without investing in banking operations themselves.
- Corporate Banking and Payroll
BaaS also extends to corporate banking and payroll management, particularly for gig economy workers and freelancers.
- Automate payroll processing, enabling instant payouts to gig workers.
- Offer benefits management, such as retirement accounts or health savings plans, embedded within the payroll platform.
This seamless integration of banking services enhances financial accessibility and convenience for both employers and workers in the gig economy.
- The Impact of BaaS on Different Sectors
BaaS is not limited to financial services; its applications stretch into multiple industries, including:
- Healthcare: Where BaaS is used to manage payments and insurance claims.
- Travel: Travel apps are incorporating BaaS to offer instant payments for bookings and refund services.
- Education: Schools and universities are using BaaS to provide tuition management and student loan services.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing BaaS
While BaaS presents numerous opportunities for innovation and growth within the fintech landscape, there are also several challenges and considerations that businesses must address when implementing BaaS solutions. Understanding these challenges is crucial for ensuring successful integration and ongoing operations. Here are some key points to consider:
The Future of BaaS: Trends and Predictions
The Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer expectations, and increasing competition in the fintech space. As we look to the future, several trends and predictions are emerging that could shape the direction of BaaS and its impact on the financial industry:
- Increased Collaboration Between Banks and Fintechs
The future will see more collaboration between traditional banks and fintech companies as they recognise the need to work together to provide comprehensive financial solutions. This collaboration can take many forms:
- Partnerships and Alliances: Banks may increasingly partner with fintechs to enhance their offerings and reach new customer segments, creating a win-win scenario for both parties.
- Shared Innovation Labs: Institutions may establish joint innovation labs to develop new products and services that leverage both banking expertise and technological innovation.
- Rise of Super Apps
The concept of super apps, which offer a wide range of services within a single platform, is gaining traction in the fintech space. These apps will likely include banking, payments, investments, insurance, and even lifestyle services. BaaS will be pivotal in enabling the integration of these diverse services, allowing companies to:
- Create All-in-One Solutions: By leveraging BaaS, companies can build super apps that provide a seamless user experience, allowing customers to manage all their financial needs in one place.
- Enhance Customer Engagement: Super apps will drive customer engagement by offering personalised financial solutions based on user behaviour and preferences.
- Focus on Customer-Centric Solutions
As competition intensifies, fintechs will increasingly focus on customer-centric solutions that prioritise user experience. This trend will be facilitated by BaaS, which enables rapid innovation and flexibility in service delivery. Key aspects of this focus include:
- Personalisation: Companies will leverage data analytics to provide personalised financial services tailored to individual customer needs, preferences, and behaviours.
- Omnichannel Experiences: Businesses will aim to deliver a seamless experience across all customer touchpoints, whether online, mobile, or in-person.
- Expansion into Emerging Markets
As the demand for digital financial services grows globally, BaaS will play a critical role in expanding into emerging markets. Key factors driving this expansion include:
- Financial Inclusion: BaaS offers the infrastructure needed to provide banking services to underserved populations, fostering greater financial inclusion.
- Local Partnerships: Fintechs will increasingly collaborate with local banks and financial institutions to navigate regulatory environments and better understand customer needs in emerging markets.
- Enhanced Security Measures
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the future of BaaS will see an increased focus on security measures. Fintechs and banks will invest in advanced security technologies and practices to protect customer data and ensure safe transactions. Anticipated developments include:
- Biometric Authentication: More companies will adopt biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, to enhance security and streamline user experiences.
- AI-Driven Fraud Detection: Artificial intelligence will play a crucial role in detecting and mitigating fraud in real time, ensuring secure financial transactions.
- Regulatory Evolution
As BaaS becomes more prevalent, regulatory frameworks will also evolve to address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this model. Expected trends include:
- Updated Regulations: Regulatory bodies may introduce new guidelines that specifically address BaaS, ensuring that both banks and fintechs maintain compliance and protect consumer interests.
- Sandbox Environments: Governments may establish regulatory sandboxes that allow fintechs to test new BaaS solutions in a controlled environment, fostering innovation while ensuring consumer protection.
- Sustainability and Ethical Banking
With growing awareness of sustainability and corporate social responsibility, BaaS providers will increasingly prioritise ethical banking practices. This will include:
- Green Financial Products: Fintechs may develop sustainable banking products that promote environmentally friendly practices, such as loans for renewable energy projects or incentives for eco-conscious behaviours.
- Transparency and Fairness: Consumers will demand greater transparency and fairness in banking practices, leading BaaS providers to adopt ethical standards in their operations.
Conclusion
As the BaaS landscape continues to evolve, companies must remain agile and responsive to emerging trends. By embracing collaboration, focusing on customer-centric solutions, and prioritizing security and compliance, businesses can position themselves for success in the ever-changing world of fintech.

